Introduction
An Ethyl Acetate manufacturing plant project report is a detailed and strategic guide for entrepreneurs and businesses interested in establishing a production facility for ethyl acetate, a widely used solvent in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries. Ethyl acetate is commonly used in applications such as coatings, adhesives, printing inks, and as a solvent in various chemical reactions. This project report provides a comprehensive overview of the production process, raw material sourcing, equipment requirements, market trends, financial projections, and regulatory guidelines to assist potential investors in setting up an efficient and profitable ethyl acetate manufacturing plant.
Overview of Ethyl Acetate
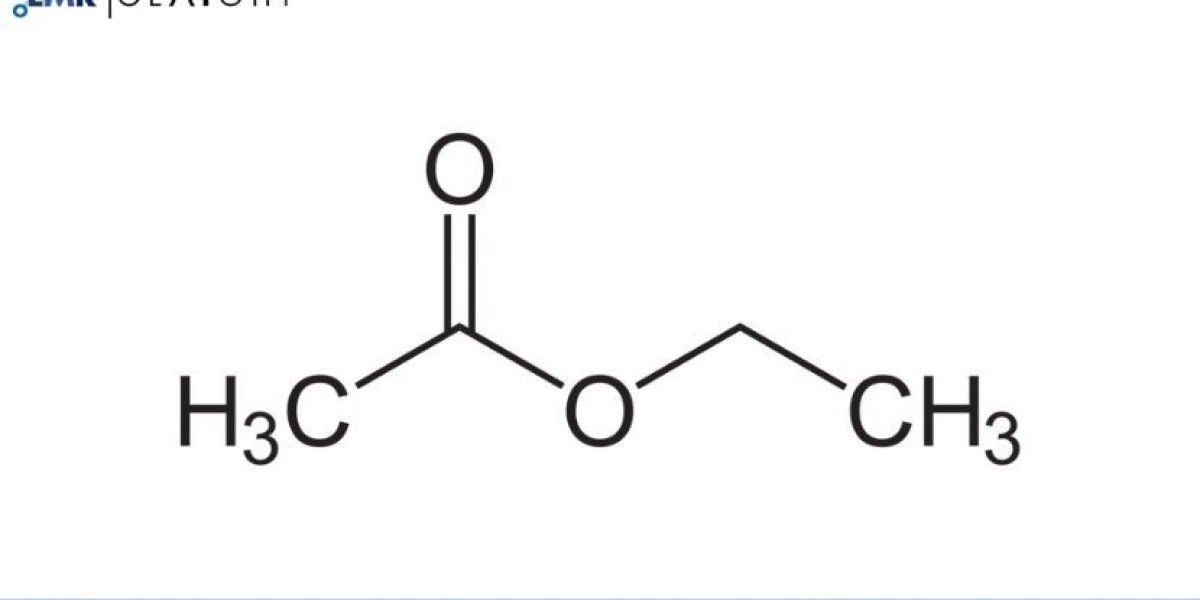
Ethyl acetate (C₄H₈O₂) is a colourless, volatile liquid with a sweet smell, often compared to the scent of pear or pineapple. It is one of the most widely used solvents in the chemical industry due to its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances, its relatively low toxicity, and its pleasant odour. Ethyl acetate is used in a variety of industries, including:
- Paints and Coatings: As a solvent in paints, varnishes, and coatings.
- Adhesives: Used in glue production for paper, leather, and plastics.
- Pharmaceuticals: Employed as a solvent in drug formulations and extractions.
- Food Industry: Used as a flavouring agent in some food products.
Ethyl acetate is also a key ingredient in the manufacture of other chemicals and is used as a cleaning agent in various industrial processes.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Manufacturing Process
The production of ethyl acetate is typically carried out through two main methods:
Esterification Process: The most common method for manufacturing ethyl acetate is the esterification of ethanol with acetic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst.
Acetylation of Ethanol with Acetic Anhydride: This is another method, where acetic anhydride reacts with ethanol, forming ethyl acetate. However, this process is less common due to the higher cost of acetic anhydride compared to acetic acid.
Raw Materials
- Ethanol: Ethanol is the primary raw material used in the production of ethyl acetate. It can be derived from natural sources like sugar cane, corn, or synthetic methods.
- Acetic Acid: Acetic acid is typically obtained through the fermentation of ethanol or via synthetic processes from petrochemical sources.
- Catalysts: Acid catalysts such as sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid are used to speed up the esterification reaction.
Equipment and Technology
- Reactor: The esterification reaction requires a reactor that can handle the temperature and pressure conditions.
- Distillation Unit: After the reaction, a distillation column is used to separate ethyl acetate from the mixture of by-products.
- Cooling System: To control the temperature of the reaction, cooling units are necessary.
- Drying Equipment: To remove any residual water, drying equipment such as molecular sieves or a drying column is used.
- Storage Tanks: For storing the final product and raw materials.
Market Demand and Trends
The demand for ethyl acetate has been steadily increasing due to its wide range of applications in various industries. Some key trends influencing the market include:
- Increased Use in Paints and Coatings: The growing demand for paints and coatings in the construction and automotive industries is driving the need for ethyl acetate.
- Growth in Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics: As a solvent, ethyl acetate plays an important role in the formulation of pharmaceutical products and cosmetics.
- Expansion of the Food and Beverage Industry: Ethyl acetate's use as a flavouring agent and in food extraction processes is contributing to its rising demand.
- Environmental Regulations: With increasing concerns about VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions, many companies are exploring alternatives, which may impact the demand for traditional solvents like ethyl acetate.
Financial Considerations
Setting up an ethyl acetate manufacturing plant involves considerable capital investment in equipment, raw materials, and operational costs. Some key financial aspects include:
- Initial Capital Investment: The cost of setting up a manufacturing plant includes purchasing machinery, constructing the facility, and obtaining necessary permits and licenses.
- Operational Costs: The ongoing costs include raw material procurement (ethanol and acetic acid), energy consumption (for heating and cooling), labour, and maintenance.
- Revenue Streams: The primary source of revenue is the sale of ethyl acetate to industries such as paints, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. Pricing is often influenced by raw material costs, demand fluctuations, and market competition.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Ethyl acetate manufacturing must comply with various safety and environmental regulations:
- Safety Standards: Due to the flammability of ethyl acetate, strict safety measures must be in place, including fire-resistant equipment, proper ventilation, and explosion-proof electrical systems.
- Environmental Compliance: The plant must adhere to regulations regarding emissions, waste disposal, and the use of hazardous chemicals.
- Health Regulations: As ethyl acetate is used in food and pharmaceutical products, the manufacturing process must meet health and safety guidelines to ensure the final product's safety.
FAQ
1. What are the main uses of ethyl acetate?
Ethyl acetate is used as a solvent in paints, coatings, adhesives, pharmaceuticals, and as a flavouring agent in food products.
2. What is the primary raw material for producing ethyl acetate?
The primary raw materials for ethyl acetate production are ethanol and acetic acid.
3. Is the production of ethyl acetate environmentally friendly?
The production process must comply with environmental regulations to limit emissions and waste. However, as a solvent, ethyl acetate is considered less harmful than many other industrial solvents.
4. What equipment is needed to manufacture ethyl acetate?
Key equipment includes reactors for esterification, distillation columns for separation, drying units, and storage tanks.
5. Can ethyl acetate be used in food products?
Yes, ethyl acetate is used as a flavouring agent and in the extraction of flavours in the food and beverage industry.
6. What are the safety concerns in manufacturing ethyl acetate?
Given its flammability, safety measures such as fire-resistant equipment, proper ventilation, and explosion-proof systems are critical in the manufacturing process.
7. What are the key challenges in the ethyl acetate manufacturing process?
Challenges include managing raw material costs, ensuring regulatory compliance, and maintaining safety standards to prevent accidents.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au